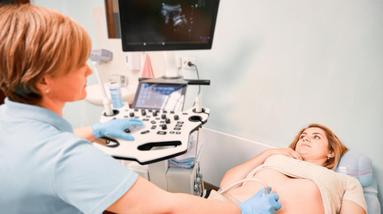
Ultrasonography, also known as ultrasound imaging, is a medical imaging technique that uses high frequency sound waves to create visual images of the internal organs and tissues of the body. During an ultrasound exam, a handheld device called a transducer is placed on the skin over the area being examined. The transducer emits sound waves that bounce off internal organs and tissues, creating echoes that are detected by the transducer and converted into visual images on a computer screen.
Ultrasonography is commonly used to evaluate the health of developing fetuses during pregnancy, as well as to diagnose a variety of medical conditions such as tumors, gallstones, and vascular disease. It is non-invasive, does not involve radiation exposure, and is generally considered to be a safe and effective diagnostic tool.