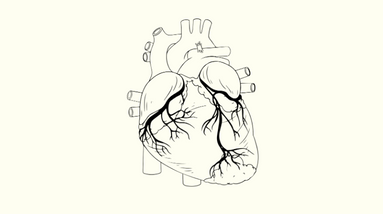
Angiography is a medical imaging procedure that uses X-rays to visualize the blood vessels in the body, including the arteries, veins, and capillaries. It is typically used to diagnose and evaluate a wide range of medical conditions, including heart disease, stroke, aneurysms, and peripheral vascular disease.
During an angiography procedure, a contrast agent, or dye, is injected into the blood vessels through a small catheter that is inserted into an artery or vein. The contrast agent makes the blood vessels visible on X-ray images, allowing healthcare providers to identify any abnormalities or blockages in the vessels.
Angiography can be performed using several different techniques, including:
Angiography is generally considered a safe and effective procedure, although there are some risks and potential complications, including bleeding, infection, allergic reaction to the contrast agent, and damage to surrounding tissue. The benefits and risks of angiography should be carefully considered and discussed with a healthcare provider.