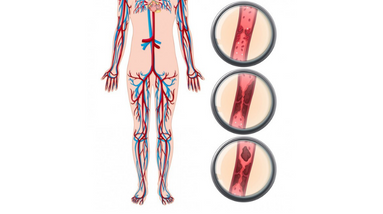
Deep vein thrombosis (DVT) is a condition that occurs when a blood clot forms in a vein deep inside the body, usually in the leg. It can cause swelling, pain, and discomfort, and in some cases, can lead to serious complications such as pulmonary embolism.
DVT is caused by a variety of factors such as prolonged immobility (for example, when traveling long distances or after surgery), injury to a vein, certain medical conditions that increase the risk of clotting (such as cancer, heart failure, or inflammatory bowel disease), and some medications that can affect blood clotting.
Symptoms of DVT may include pain, swelling, redness, and warmth in the affected leg, but some people with DVT may not have any symptoms. If the blood clot breaks off and travels to the lungs, it can cause a life-threatening condition called pulmonary embolism, which can cause shortness of breath, chest pain, and fainting.
Treatment for DVT typically involves anticoagulant medications, which thin the blood and prevent further clots from forming. In some cases, additional procedures such as the insertion of a filter into the vena cava (the large vein that carries blood from the lower body to the heart) may be necessary to prevent pulmonary embolism. It’s important to seek medical attention if you suspect that you may have DVT to prevent further complications.