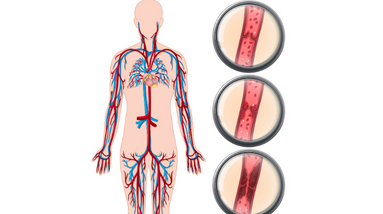
Carotid artery disease is a condition in which the carotid arteries, which are the blood vessels in the neck that supply blood to the brain, become narrowed or blocked. This can reduce blood flow to the brain and increase the risk of stroke.
The most common cause of carotid artery disease is atherosclerosis, which is a buildup of plaque in the inner lining of the artery wall. Other factors that can contribute to the development of carotid artery disease include high blood pressure, high cholesterol, smoking, diabetes, and a family history of the condition.
Symptoms of carotid artery disease may include weakness or numbness on one side of the body, trouble speaking or understanding speech, vision problems, and severe headaches. However, in some cases, there may be no symptoms at all.
Treatment for carotid artery disease may involve lifestyle changes such as quitting smoking, eating a healthy diet, and exercising regularly. Medications such as blood thinners and cholesterol-lowering drugs may also be prescribed. In some cases, a procedure called carotid endarterectomy may be recommended to remove the plaque buildup from the carotid artery and improve blood flow to the brain.
It’s important to seek medical attention if you have any symptoms of carotid artery disease or if you have risk factors for the condition. Early detection and treatment can help reduce the risk of stroke and other complications.