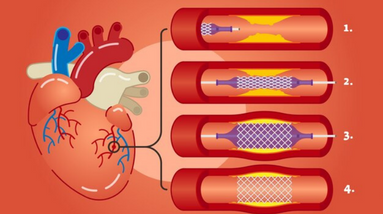
Coronary angioplasty is a minimally invasive procedure used to treat narrowed or blocked coronary arteries in the heart. During the procedure, a catheter is inserted into a blood vessel, typically in the groin, and guided to the blocked artery. A small balloon attached to the catheter is then inflated to open up the artery and improve blood flow to the heart.
In some cases, a stent may also be inserted into the artery to help keep it open. This is known as a stenting procedure.
Coronary angioplasty is used to treat a variety of heart conditions, including angina, acute coronary syndrome, and heart attack. It can help improve blood flow to the heart, reduce symptoms, and lower the risk of future heart problems.
Coronary angioplasty is generally considered safe and effective, with a high success rate in improving blood flow to the heart and reducing symptoms. However, there are some risks and potential complications associated with the procedure, including bleeding, infection, allergic reaction to the contrast agent used during the procedure, and re-narrowing or blockage of the artery. The benefits and risks of coronary angioplasty should be carefully considered and discussed with a healthcare provider.