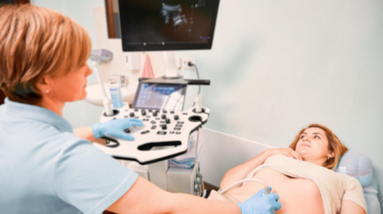
Abdominal ultrasonography is a medical imaging technique that uses high frequency sound waves to produce images of the internal structures of the abdomen, including the liver, gallbladder, pancreas, spleen, kidneys, and bladder. It can help diagnose various conditions, such as liver disease, gallstones, kidney stones, abdominal tumors, and other abdominal abnormalities. During the procedure, a handheld device called a transducer is placed on the abdomen, which emits sound waves and detects their echoes as they bounce back from the internal organs. The echoes are then converted into images by a computer, which can be viewed on a monitor. Abdominal ultrasonography is noninvasive, painless, and does not expose patients to ionizing radiation.